Project management involves meticulous planning and scheduling to ensure the successful completion of a project within the allotted time frame. Two key concepts in project scheduling are the critical path and the driving path. While these terms may sound similar, they have distinct meanings and play important roles in project management. In this article, we will explore the differences between the critical path and the driving path, shedding light on their significance in project scheduling and execution.
Critical Path
The critical path represents the longest sequence of tasks or activities that must be completed to finish a project, considering their durations and dependencies. It determines the minimum time required to complete the project. Tasks on the critical path have zero slack or float time, which means any delay in their completion will directly impact the overall project timeline. Therefore, identifying and managing the critical path is crucial to ensuring timely completion of the project. Key characteristics of the critical path include:
- Determines Project Duration: By identifying the critical path, project managers can determine the project’s expected duration and set realistic timelines for completion.
- Resource Allocation: The critical path plays a crucial role in allocating resources efficiently. Project managers can prioritize the tasks on the critical path to ensure the availability of resources when they are most needed. By closely monitoring the critical path, project managers can identify potential bottlenecks, allocate resources effectively, and identify opportunities for optimization.
- Impact of Delays: Since tasks on the critical path have no slack time, any delay in their execution will delay the project’s completion. Thus, careful monitoring and management of critical path tasks are essential to keep the project on track.
Driving Path
The driving path, on the other hand, is a term used to describe the sequence of activities that are essential to meet a specific milestone or target date within the project. Unlike the critical path, the driving path may not necessarily be the longest path in the network diagram. It is determined based on the activities that have a significant impact on achieving a particular goal or completing a specific deliverable by the desired deadline. By focusing on the driving path, project managers can allocate resources and prioritize efforts to ensure the timely accomplishment of critical milestones. Key characteristics of the driving path include:
- Focus on Crucial Milestone: The driving path allows project managers to focus their attention on the most important tasks that directly contribute to meeting crucial milestones.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: By focusing on the driving path, project teams can allocate resources strategically, optimize efforts, and ensure timely completion of significant project deliverables.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: This approach helps maintain project momentum, enhances stakeholder satisfaction, and allows for effective project progress tracking.
- Timely Completion: By prioritizing the tasks on the driving path, project managers can ensure that the critical activities are completed within the planned time frame. This helps maintain project momentum and avoids bottlenecks.
Example
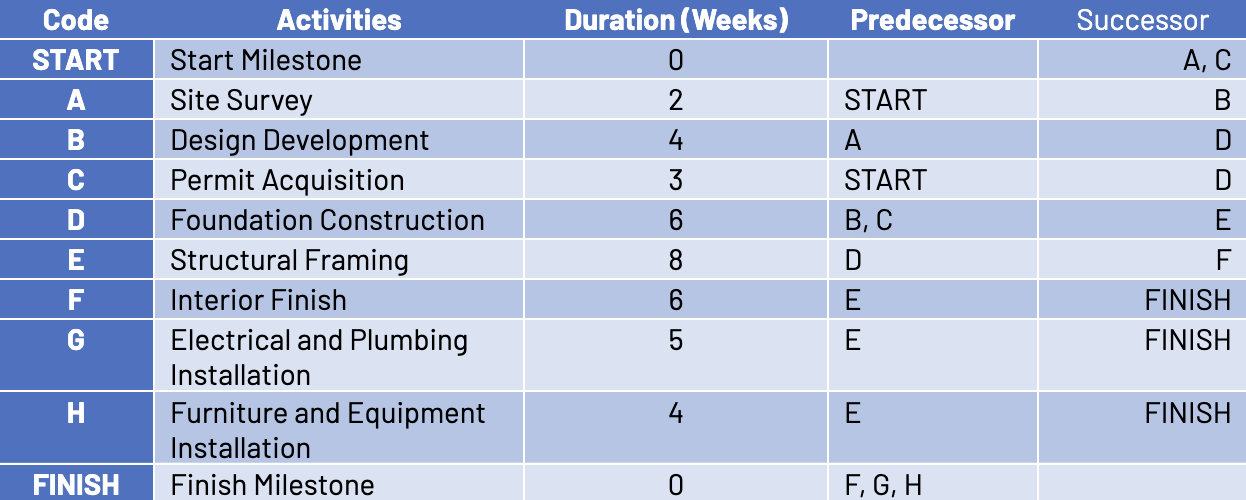
Consider a situation in which you are building a new office facility. The below table contains the high-level list of activities, durations, and logic needed to complete the project.
In this example, the Critical path is “START → A → B → D → E → F → FINISH”, which totals 26 weeks. This path has the longest duration as well as zero total slack/float, hence, any delay in activities along this path would result in the delay of the project.
On the other hand, the Driving path focuses on specific milestones or target dates within the project. For example, in this case, the same building project has two important milestones to the client:
- Milestone 1: Completion of Foundation Construction within 12 weeks
- Milestone 2: Completion of Structural Framing within 20 weeks
The driving path for Milestone 1 is “START → A → B → D” while the driving path for Milestone 2 is “START → A → B → D → E” for Milestone 2. These activities are critical to meeting the respective milestones on time.
Conclusion
The critical path and driving path are fundamental concepts in project scheduling, each serving a distinct purpose. The critical path determines the overall project duration and guides project managers in allocating resources and monitoring potential delays, while the driving path focuses on the activities necessary to achieve specific milestones or target dates within the project. Understanding both paths enables project managers to optimize project schedules, minimize delays, and deliver successful outcomes. By leveraging the knowledge of the critical path and driving path, project teams can effectively plan, execute, and control projects, ensuring they are completed on time and on budget.
At Front Line Advisory Group, we provide program management consulting services for capital improvement bonds. We are revolutionizing the construction industry and transforming client expectations by obsessing over the basics of budget oversight, schedule enforcement, compliance, vendor management, and stakeholder communication. Contact us for more info at info@frontlineadvisorygroup.com.