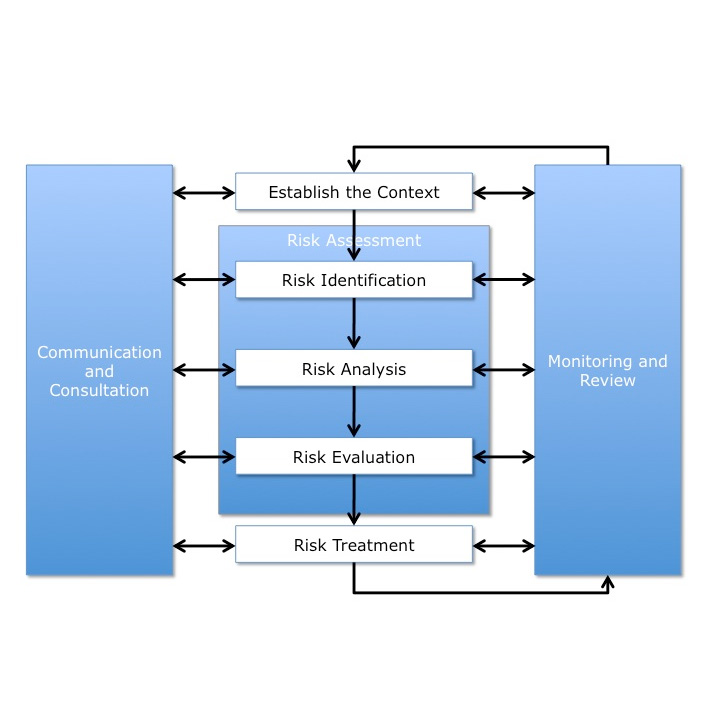
Effective local service delivery underpins all thriving Texan communities. As municipalities across the State of Texas seek innovative avenues to fund and manage essential services like water supply, sewage systems, waste disposal, and public spaces maintenance, two strategies are gaining traction: the utilization of municipal user fees and the establishment of Municipal Utility Districts (MUDs). Tailored to align with Texas state laws and codes governing municipal authority and finance, these approaches not only ensure equitable funding but also empower jurisdictions to tailor services to their unique requirements. In this article, we delve into the benefits and specific considerations associated with implementing these strategies, shedding light on how they can contribute to the holistic development of municipalities within the Lone Star State.
Municipal User Fees: Navigating Texas State Regulations
Municipal user fees, charges imposed on residents and businesses for specific services, have emerged as a robust solution within the framework of state laws and municipal code. These fees are closely aligned with Texas Local Government Code provisions, enabling municipalities to distribute the financial responsibility fairly among those directly benefiting from the services. Common services covered by user fees in Texas include water consumption, waste management, and recreational facilities usage.
An advantage unique to Texas is the feasibility of cost recovery within the boundaries of state laws. These user fees, distinct from general taxes that fund diverse services, are intrinsically linked to the utilization of particular services. This connection ensures the funds collected are exclusively allocated to the enhancement and maintenance of the services themselves. For instance, under the Texas Water Code, fees generated from water consumption can be channeled into upgrades for water treatment infrastructure or the augmentation of water distribution networks.
Furthermore, user fee systems stimulate resource conservation, a particularly significant consideration given the state’s arid climate. With charges based on usage, individuals are inclined to adopt more responsible consumption habits. Elevated consumption rates translate to higher bills, creating an incentive for residents and businesses to implement water-saving technologies or environmentally-conscious practices.
However, municipalities must address the challenge of affordability, especially for low-income households. To mitigate this concern, municipalities can structure fees progressively, wherein charges vary based on consumption levels. This safeguard ensures that basic service accessibility remains affordable for all Texans, irrespective of income.
Municipal Utility Districts: Aligning with Texan Governance
Municipal Utility Districts (MUDs), established as local government entities, provide specific services, often focusing on utilities such as water supply, sewage systems, and stormwater management. In the context of Texas state laws, MUDs empower communities by enabling tailored service solutions that adhere to the intricacies of Texan governance.
A significant advantage of MUDs is their alignment with Texan values regarding local control. Communities have the autonomy to customize services in accordance with their distinctive needs, enabling prompt response to evolving conditions. For example, a rapidly growing neighborhood can opt for expedited infrastructure expansion to accommodate population growth, while a more established area might prioritize the sustainability and upkeep of existing facilities.
MUDs are also well-positioned to drive innovation, capitalizing on localized flexibility. Operating within a defined geographical scope, MUDs can experiment with cutting-edge technologies or sustainable practices that resonate with the community’s priorities. This localized approach expedites the implementation of innovative solutions without the administrative complexities associated with larger-scale municipal operations.
Regarding funding, MUDs possess the authority to issue bonds to finance infrastructure projects. These bonds are repaid over time using revenues derived from user fees, ensuring that the responsibility of repayment rests with those directly reaping the benefits. This financial independence empowers MUDs to make long-term investments without straining the broader municipal budget, in line with Texas laws.
Challenges and Considerations
While both municipal user fees and MUDs offer compelling advantages, there are specific challenges that necessitate consideration during their implementation.
Public Engagement: Successful integration of user fees or MUDs hinges on effective public engagement. Transparent communication is paramount to ensuring communities comprehend the rationale behind these strategies and the potential gains they offer.
Equity in Fees: Municipalities must ensure that user fees do not disproportionately affect low-income households. Progressive fee structuring and the provision of exemptions or subsidies are essential to uphold accessibility to vital services.
Governance and Accountability: MUDs must adhere to transparent operations and be accountable to the communities they serve. Establishing unambiguous governance structures and avenues for public oversight is crucial to forestall misallocation of funds and ensure effective service delivery.
Long-Term Planning: Both user fees and MUDs necessitate prudent long-term planning, particularly within the context of Texas’s dynamic growth landscape. Anticipating factors such as population expansion and infrastructure maintenance is crucial to prevent service gaps and financial strain.
In the face of evolving urban challenges and limited resources, Texan municipalities must explore innovative avenues for delivering essential services to their residents. By employing municipal user fees and establishing Municipal Utility Districts in harmony with Texas state laws and codes governing municipal authority and finance, municipalities can harness equitable funding mechanisms and localized service solutions. These strategies contribute to the welfare of Texan communities and pave the way for more sustainable, efficient, and locally-responsive service delivery systems.
At Front Line Advisory Group, we provide program management consulting services for capital improvement bonds. We are revolutionizing the construction industry and transforming client expectations by obsessing over the basics of budget oversight, schedule enforcement, compliance, vendor management, and stakeholder communication. Contact us for more info at info@frontlineadvisorygroup.com.