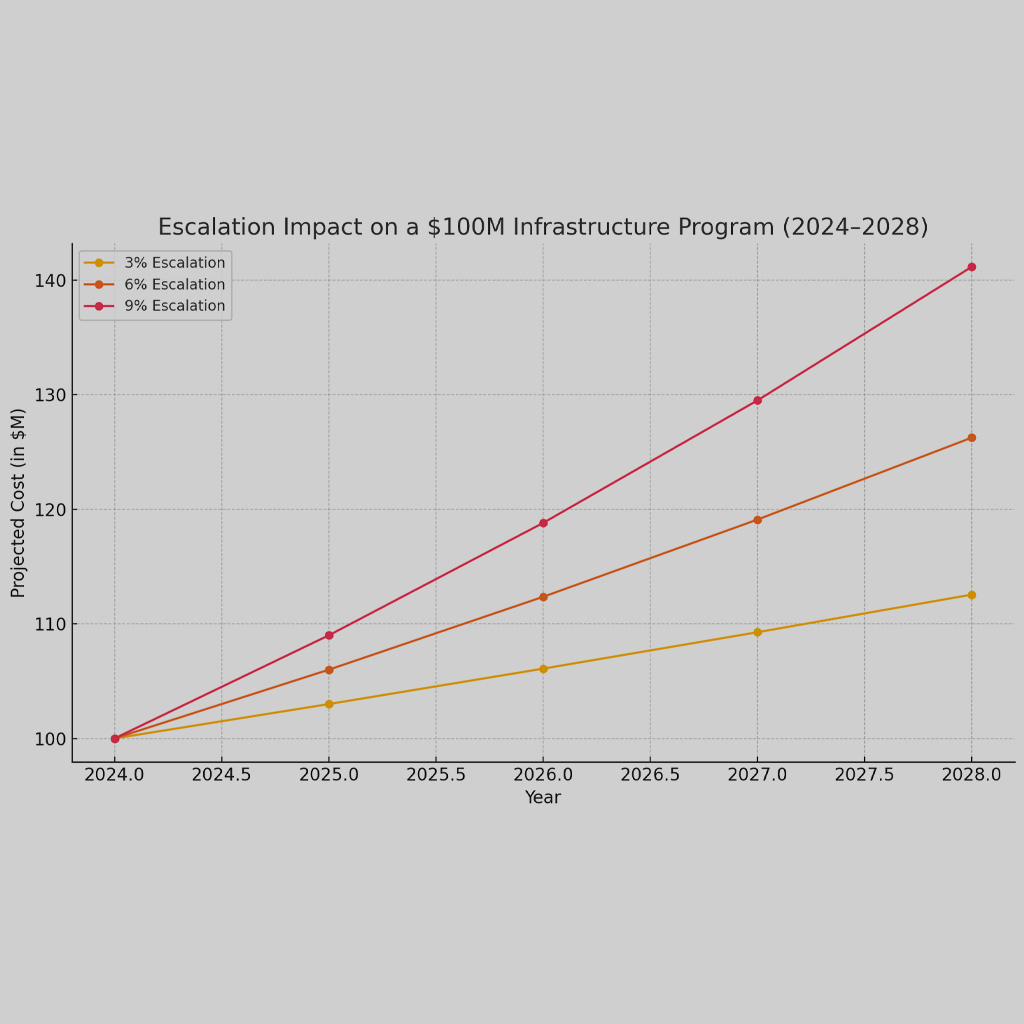
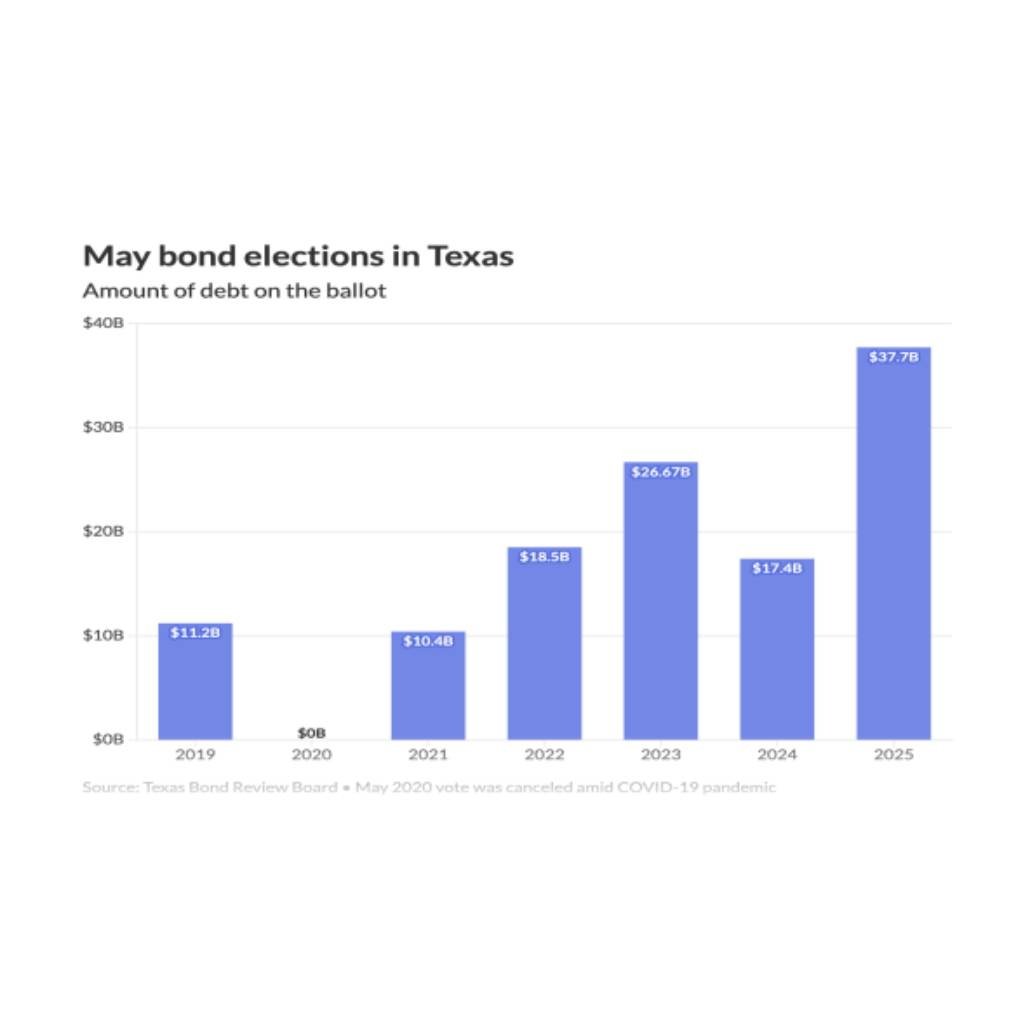
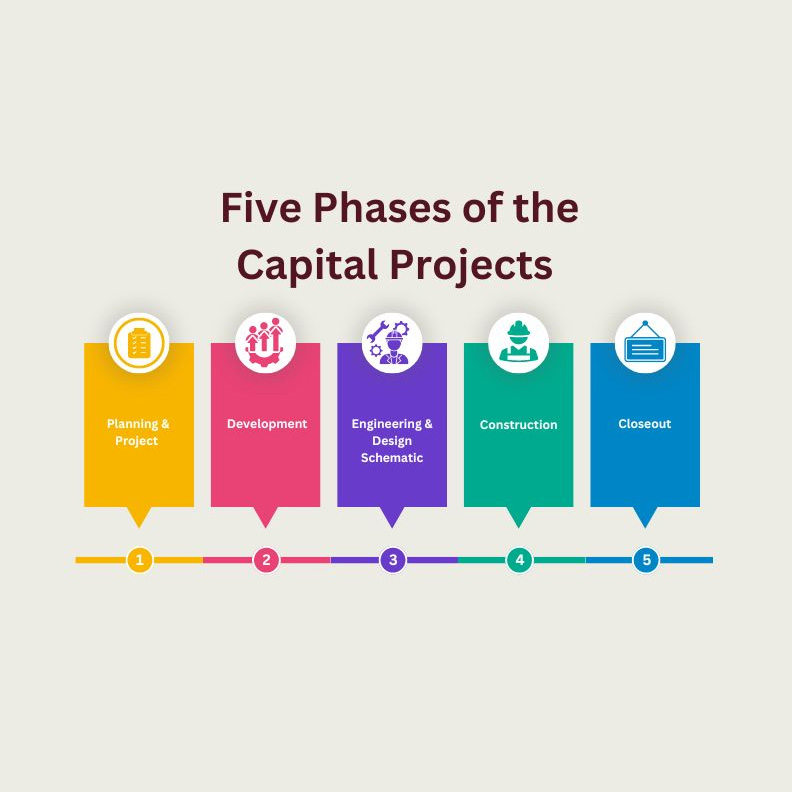
“No great thing is created suddenly.” -Epictetus
Understanding the US Defense Contracting Management Agency (DCMA-14) and Its Application to Capital Improvement Program (CIP) Bond Management
The US Defense Contracting Management Agency (DCMA) plays a pivotal role in ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of defense procurement. The DCMA’s practices, particularly those encapsulated in DCMA-14, provide a framework that can be highly beneficial for managing Capital Improvement Program (CIP) bonds. CIP bonds are crucial for funding infrastructure projects, and their management requires rigorous oversight, effective communication, and stringent compliance measures. This article explores the DCMA-14 framework and its potential application to CIP bond management.
Understanding DCMA-14
The DCMA-14 is a set of guidelines and best practices established by the DCMA to enhance contract management and oversight. These guidelines focus on key areas such as contract administration, supplier risk management, cost and schedule control, quality assurance, and compliance with federal regulations. The primary objective of DCMA-14 is to ensure that defense contracts are executed efficiently, within budget, and on schedule while maintaining high standards of quality and compliance.
Key Components of DCMA-14
- Contract Administration: This involves the meticulous oversight of contract performance, including regular reviews and audits to ensure adherence to contract terms and conditions.
- Supplier Risk Management: DCMA-14 emphasizes the importance of identifying and mitigating risks associated with suppliers. This includes evaluating the financial health, performance history, and reliability of suppliers.
- Cost and Schedule Control: Implementing robust cost control measures and maintaining strict adherence to project schedules are central to DCMA-14. This involves regular monitoring and reporting to ensure projects stay on track.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring that the products and services delivered meet specified quality standards is a critical aspect of DCMA-14. This involves rigorous testing, inspections, and quality audits.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to federal regulations and contractual obligations is fundamental to DCMA-14. This includes compliance with financial reporting requirements, environmental regulations, and other statutory obligations.
Applying DCMA-14 to CIP Bond Management
The principles and practices of DCMA-14 can be effectively applied to the management of CIP bonds, which fund infrastructure projects for municipalities and schools. Here’s how DCMA-14 can enhance CIP bond management:
- Enhanced Contract Administration In CIP bond management, robust contract administration is crucial. Applying DCMA-14’s principles can ensure that contracts are executed as per the agreed terms. This includes regular performance reviews, audits, and timely resolution of any issues. By adopting these practices, CIP managers can enhance transparency and accountability, ensuring that all stakeholders are informed about project progress and any deviations from the plan.
- Supplier Risk Management Infrastructure projects often involve multiple suppliers and contractors. Implementing DCMA-14’s supplier risk management practices can help CIP managers identify potential risks early and develop mitigation strategies. Evaluating the financial stability, past performance, and reliability of suppliers can prevent delays and cost overruns, ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Cost and Schedule Control One of the biggest challenges in CIP bond management is maintaining control over costs and schedules. DCMA-14’s emphasis on regular monitoring and reporting can help CIP managers keep projects on track. By establishing clear benchmarks and conducting frequent reviews, managers can quickly identify and address any issues that may cause delays or budget overruns.
- Quality Assurance Ensuring the quality of construction and infrastructure is paramount. Applying DCMA-14’s rigorous quality assurance measures can help CIP managers maintain high standards. This includes regular inspections, testing, and quality audits to ensure that all work meets the required specifications and standards. High-quality infrastructure not only ensures public safety but also enhances the longevity and sustainability of projects.
- Regulatory Compliance CIP bond projects must comply with a myriad of federal, state, and local regulations. Adopting DCMA-14’s comprehensive approach to regulatory compliance can help CIP managers navigate these requirements efficiently. This includes maintaining accurate financial records, adhering to environmental regulations, and ensuring compliance with all contractual obligations.
Conclusion
The US Defense Contracting Management Agency’s DCMA-14 framework offers a robust set of practices that can significantly enhance the management of Capital Improvement Program bonds. By adopting these principles, CIP managers can improve contract administration, manage supplier risks, control costs and schedules, ensure quality, and comply with regulatory requirements. Implementing DCMA-14 can transform CIP bond management, leading to more efficient, effective, and transparent project execution. This, in turn, can help municipalities and schools deliver high-quality infrastructure projects that meet the needs of their communities, on time and within budget.
References
- Defense Contract Management Agency (DCMA). (n.d.). DCMA Manual 14-1 – Contract Management Manual. Retrieved from DCMA.mil
- U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO). (2020). Defense Contracting: Actions Needed to Improve the Defense Contract Management Agency’s Oversight. Retrieved from GAO.gov
- Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR). (n.d.). Retrieved from Acquisition.gov
By applying these established principles, the complexities and challenges of CIP bond management can be effectively addressed, ensuring successful project outcomes and improved community infrastructure.