Introduction to Capital Improvement Program
A capital improvement program (CIP) is a strategic plan that outlines the long-term investments and projects required to improve and maintain the infrastructure of a business, city, or organization. It serves as a roadmap for identifying, prioritizing, and funding essential projects that enhance the quality of life for residents, employees, and stakeholders.
Definition and purpose of a capital improvement program
At its core, a capital improvement program is designed to address the ongoing needs of an entity’s physical assets. These assets can include buildings, roads, utilities, parks, technology systems, and more. The purpose of implementing a capital improvement program is two-fold: to ensure the efficient functioning and longevity of these assets while also meeting the evolving needs of the community or organization.
By developing a comprehensive CIP, businesses can proactively plan for necessary improvements rather than reacting to emergencies or unexpected failures. This proactive approach helps minimize disruptions in operations and reduces costs associated with reactive maintenance. Additionally, a well-thought-out CIP can enhance the overall value and attractiveness of an entity by creating an environment that supports growth and development.
A capital improvement program also plays a vital role in fostering economic development. By investing in infrastructure improvements such as transportation networks or public facilities, cities can attract new businesses and industries. These investments create jobs, stimulate economic growth, and improve the overall quality of life for residents.
In summary, a capital improvement program is an essential tool for managing physical assets efficiently while meeting the evolving needs of businesses, cities, or organizations. It provides a strategic framework for identifying priorities and allocating resources effectively. By implementing a CIP, entities can ensure their long-term success by maintaining infrastructure integrity while supporting growth and development within their communities.
Steps in Creating a Capital Improvement Program
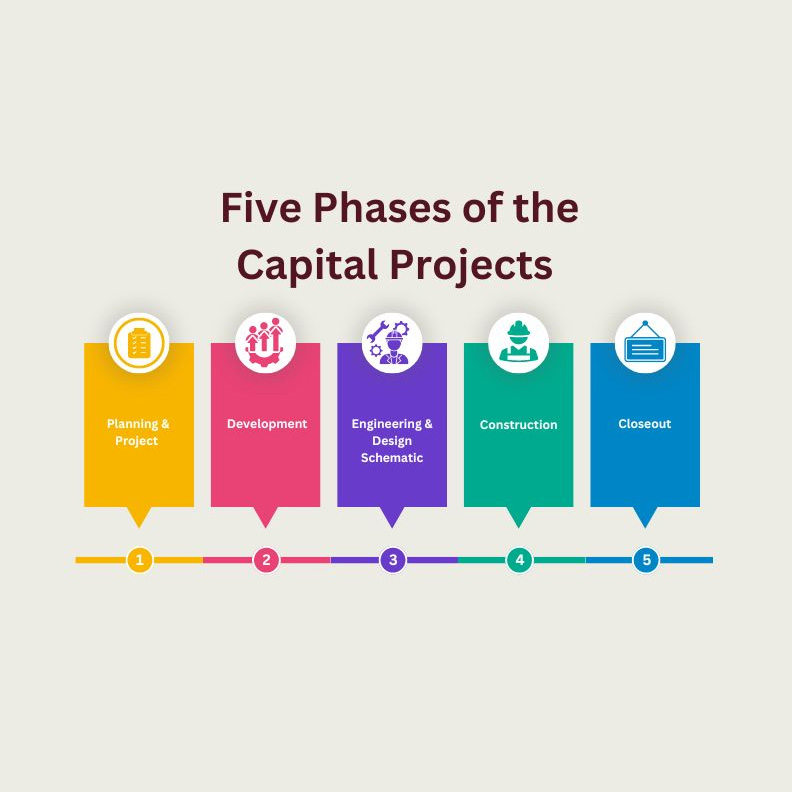
A capital improvement program (CIP) is a long-term plan that outlines the investment of funds into infrastructure projects and other physical assets. It helps organizations and municipalities prioritize their investments and allocate resources efficiently. The process of creating a CIP involves several steps, each crucial for its successful implementation. In this section, we will outline the five key steps involved in creating a capital improvement program.
Step 1: Assessing current assets and needs
Before embarking on the creation of a capital improvement program, it is essential to assess the organization’s or municipality’s existing assets and identify areas that require improvement or investment. This assessment provides valuable insights into the current state of infrastructure, facilities, equipment, and other physical assets.
To conduct an asset assessment effectively, organizations can employ various methods and tools. One common approach is conducting physical inspections to evaluate the condition of assets. This can involve visual inspections, surveys, or even using specialized equipment for more accurate assessments.
Additionally, data analysis plays a crucial role in assessing current assets and needs. Analyzing historical data related to maintenance costs, repair frequency, and performance indicators can help identify areas that require immediate attention.
By assessing existing assets and identifying needs early on in the process, organizations can develop a comprehensive understanding of their infrastructure requirements. This information forms the foundation for setting goals and priorities in the next step of creating a capital improvement program.
Step 2: Establishing goals and priorities
Once the assessment phase is complete, organizations need to establish clear goals and priorities for their capital improvement program. Setting goals ensures that investments align with broader organizational objectives while prioritizing helps determine where resources should be allocated first.
When establishing goals for a CIP, it is essential to consider factors such as economic development plans, community needs, environmental sustainability targets, safety requirements, and regulatory compliance. These factors provide guidance on which projects should be prioritized based on their potential impact and alignment with broader objectives.
Prioritization can be a complex process, as it involves evaluating projects based on various criteria. Some common factors to consider include the urgency of repairs or upgrades, the potential for cost savings or revenue generation, and the level of stakeholder support.
By setting clear goals and priorities, organizations ensure that their capital improvement program is focused and aligned with their overall vision. This step lays the groundwork for developing a budget and funding plan in the next phase.
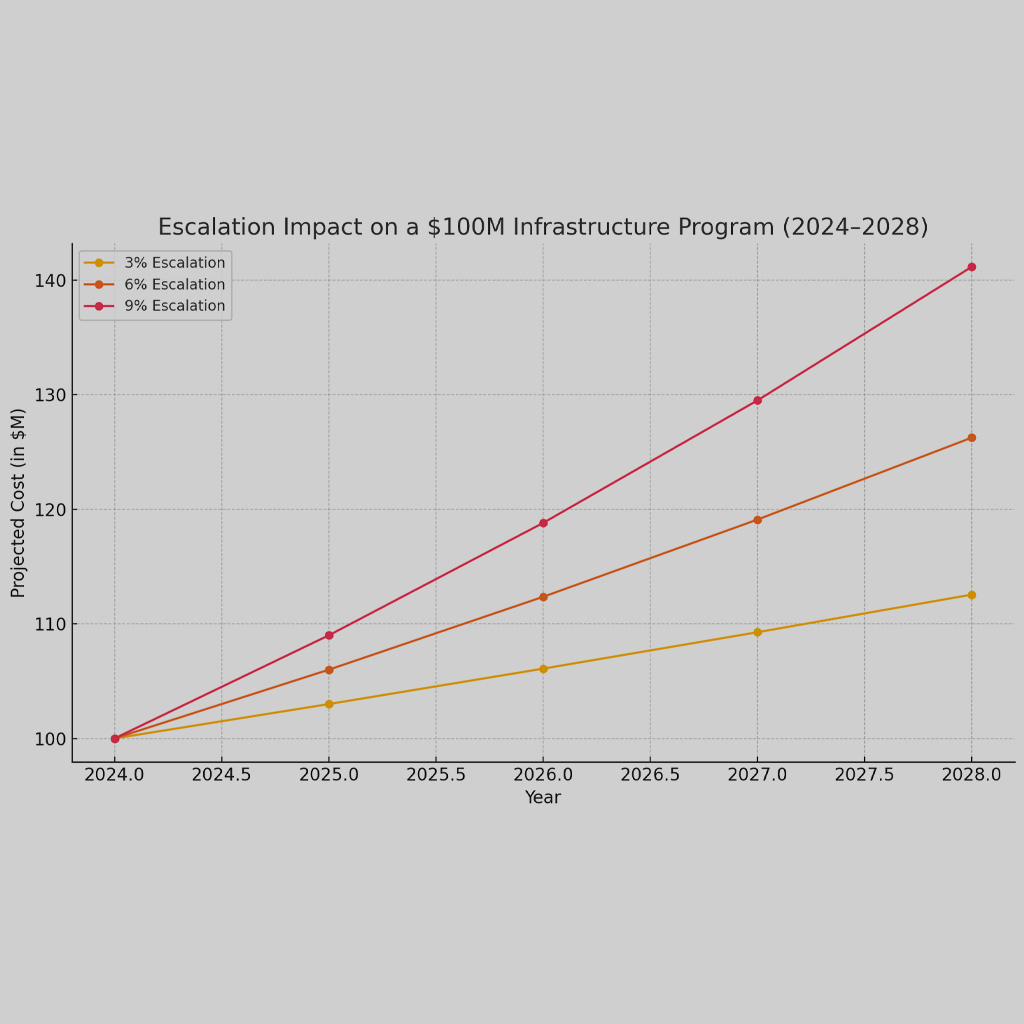
Step 3: Developing a budget and funding plan
Creating a budget for a capital improvement program requires careful consideration of available financial resources and projected costs. It involves estimating the total investment required to achieve the established goals and priorities.
To develop an accurate budget, organizations need to consider both one-time project costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. One-time costs include construction or renovation expenses, equipment purchases, and any necessary permits or licenses. Ongoing costs may include routine maintenance, staff training, energy consumption, or other operational expenses.
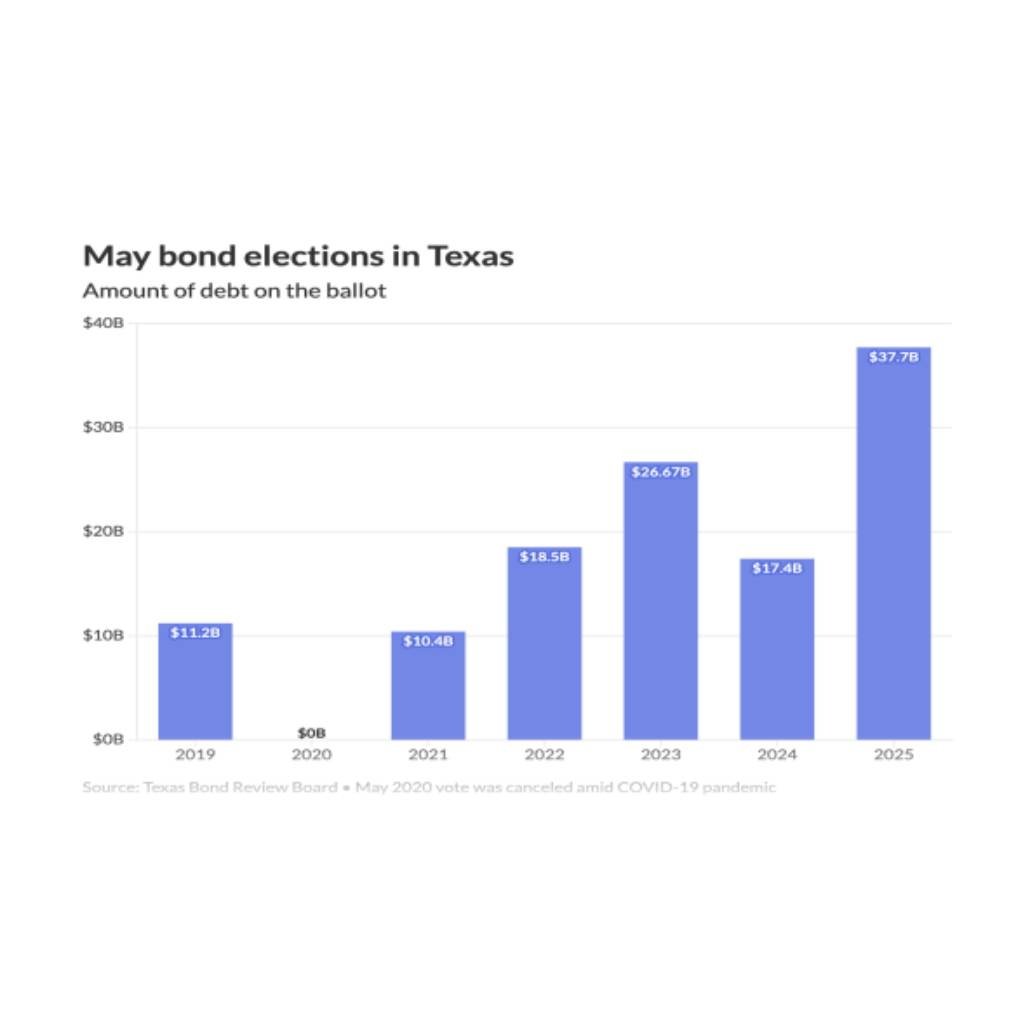
In addition to estimating costs, organizations must also identify potential sources of funding for their capital improvement program. These sources can vary depending on the organization’s nature (public or private) and its specific circumstances. Common funding sources include government grants, bonds or loans, public-private partnerships, impact fees, user charges, or fundraising initiatives.
Developing a comprehensive funding plan involves exploring different strategies for securing financial resources. Organizations may need to engage with stakeholders such as investors, financial institutions, community members, or government agencies to secure necessary funding.
By creating a well-defined budget and funding plan for their capital improvement program, organizations can ensure that they have the necessary financial resources to implement projects effectively.
Step 4: Implementing the program
Once the budget and funding plan are in place, organizations can move forward with implementing their capital improvement program. This phase involves executing planned projects according to predefined timelines and milestones.
Project management techniques and best practices play a crucial role in the successful implementation of a capital improvement program. Organizations need to establish project teams, assign responsibilities, and develop detailed project plans. Regular communication and coordination among team members are essential to ensure smooth execution.
During the implementation phase, organizations may encounter various challenges such as unexpected delays, budget constraints, or changes in stakeholder requirements. It is crucial to have contingency plans in place to address these challenges effectively.
Effective project monitoring and control mechanisms should be established to track progress and ensure that projects stay on schedule and within budget. Regular reporting and performance evaluations help identify any deviations from the original plan and enable timely corrective actions.
By effectively implementing their capital improvement program, organizations can bring their planned projects to fruition, resulting in improved infrastructure, enhanced facilities, or upgraded equipment.
Step 5: Monitoring and evaluating progress
Monitoring and evaluating the progress of a capital improvement program is vital for its long-term success. This step involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the effectiveness of implemented projects and identify areas for further improvement.
Organizations should define relevant KPIs based on their specific goals and priorities. These indicators can include metrics such as cost savings achieved, energy efficiency improvements, customer satisfaction ratings, or asset condition assessments.
Regular monitoring allows organizations to identify any issues or bottlenecks early on during the implementation phase. By addressing these issues promptly, organizations can minimize potential disruptions and optimize resource allocation.
Evaluation plays a critical role in determining whether the capital improvement program has achieved its intended outcomes. It helps assess the overall impact of investments made through the CIP by comparing actual results against predefined targets or benchmarks.
Based on evaluation findings, organizations can make informed decisions about future investments or adjustments to existing projects. Continuous monitoring and evaluation provide valuable insights for refining future capital improvement programs.
Importance of Stakeholder Involvement
Involving stakeholders in the capital improvement program process is crucial for its success. By including various individuals and groups who have a vested interest in the program, decision-making can be improved and project outcomes can be more successful. There are several benefits to involving stakeholders in the capital improvement program process.
Firstly, stakeholder involvement leads to better decision-making. When individuals who will be affected by the program are included in the decision-making process, their input and perspectives can provide valuable insights. They may offer unique knowledge or expertise that can help shape decisions and ensure that all aspects of the program are considered. This collaborative approach promotes a sense of ownership among stakeholders and increases their commitment to the program’s success.
Additionally, involving stakeholders fosters collaboration and builds relationships. When stakeholders feel heard and valued, they are more likely to actively participate in discussions and contribute their ideas. This collaborative environment encourages open communication, trust, and cooperation among all parties involved. By working together towards a common goal, stakeholders can pool their resources, share information, and leverage their collective expertise to overcome challenges and find innovative solutions.
Furthermore, stakeholder involvement helps to identify potential issues or concerns early on in the process. Stakeholders often have firsthand knowledge of specific needs or challenges within their communities or organizations that may impact the success of the capital improvement program. By engaging with them from the beginning, these issues can be identified and addressed proactively. This proactive approach minimizes delays, reduces costs associated with rework or modifications later on, and ensures that the final program meets the needs of all stakeholders involved.
Lastly, involving stakeholders enhances transparency and accountability throughout the entire capital improvement program process. When stakeholders have a seat at the table during decision-making processes, they can witness firsthand how decisions are made and understand why certain choices were made. This transparency builds trust among stakeholders as they see that their input is valued and considered when making important decisions.
In conclusion, involving stakeholders in the capital improvement program process is essential for its success. The benefits of stakeholder involvement include improved decision-making, collaboration, early issue identification, and enhanced transparency and accountability. By actively engaging stakeholders throughout the process, business owners, city planners, and project managers can ensure that their capital improvement programs are well-informed,
At Front Line Advisory Group, we are pioneers in Capital Improvement Bond Management, leveraging unparalleled expertise and deep industry insights. Our mission extends beyond consultation – we empower our clients to realize the full potential of their investments, ensuring tax dollars are put to maximum use through astute Program Management Consulting. For more information or to commence your journey towards transformative bond management, reach out to us at info@frontlineadvisorygroup.com